Artificial Intelligence & Data Analysis
Group project
Timeline
- Before March, 18: Make groups of 2 people and fill the following Google sheet:
- Pick a group id (you can choose the one you want, not important).
- Specify group member names.
- Rank each of the 8 projects from most wanted (1) to least wanted (8).
- April, 9: Oral presentation (10 min + 5 min for questions).
Compute
You can choose among 2 options:
- Use your own laptop, particularly if you have a GPU.
- Google Colab is a way to access a GPU for free.
List of subjects
Below is the list of subjects you can choose from. Please note that two groups can’t work on the same subject!
1. Handwritten digits classification (Computer Vision, Supervised learning)
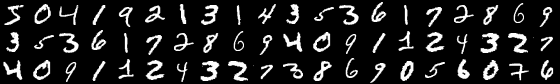
Data
You can use the code below to create train and test Pytorch datasets. It is then your job to explore the provided data. Also, don’t forget to create a proper validation set from a part of your training data.
import torchvision
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
"data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
"data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
Project milestones
You will have to properly do the following:
- Building a training/validation/test data split. Do not change the provided test set. You should keep the official test set of the task!
- Validating your model and training hyperparameters on the validation set.
- Testing your best model (based on the validation performance) on the test set. For this, you’ll go beyond simple loss and accuracy metrics, but will also consider other metrics.
- Visualizing the outputs of your model, and understanding its errors.
2. Handwritten letters classification (Computer Vision, Supervised learning)

Data
You can use the code below to create train and test Pytorch datasets. It is then your job to explore the provided data. Also, don’t forget to create a proper validation set from a part of your training data.
import torchvision
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.EMNIST(
"data",
split="letters",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.EMNIST(
"data",
split="letters",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
Project milestones
You will have to properly do the following:
- Building a training/validation/test data split. Do not change the provided test set. You should keep the official test set of the task!
- Validating your model and training hyperparameters on the validation set.
- Testing your best model (based on the validation performance) on the test set. For this, you’ll go beyond simple loss and accuracy metrics, but will also consider other metrics.
- Visualizing the outputs of your model, and understanding its errors.
3. Japanese symbols classification (Computer Vision, Supervised learning)

Data
You can use the code below to create train and test Pytorch datasets. It is then your job to explore the provided data. Also, don’t forget to create a proper validation set from a part of your training data.
import torchvision
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.KMNIST(
"data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.KMNIST(
"data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
Project milestones
You will have to properly do the following:
- Building a training/validation/test data split. Do not change the provided test set. You should keep the official test set of the task!
- Validating your model and training hyperparameters on the validation set.
- Testing your best model (based on the validation performance) on the test set. For this, you’ll go beyond simple loss and accuracy metrics, but will also consider other metrics.
- Visualizing the outputs of your model, and understanding its errors.
4. Clothing articles classification (Computer Vision, Supervised learning)

Data
You can use the code below to create train and test Pytorch datasets. It is then your job to explore the provided data. Also, don’t forget to create a proper validation set from a part of your training data.
import torchvision
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
"data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
"data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
)
Project milestones
You will have to properly do the following:
- Building a training/validation/test data split. Do not change the provided test set. You should keep the official test set of the task!
- Validating your model and training hyperparameters on the validation set.
- Testing your best model (based on the validation performance) on the test set. For this, you’ll go beyond simple loss and accuracy metrics, but will also consider other metrics.
- Visualizing the outputs of your model, and understanding its errors.
5. Mountain Car (Reinforcement Learning)
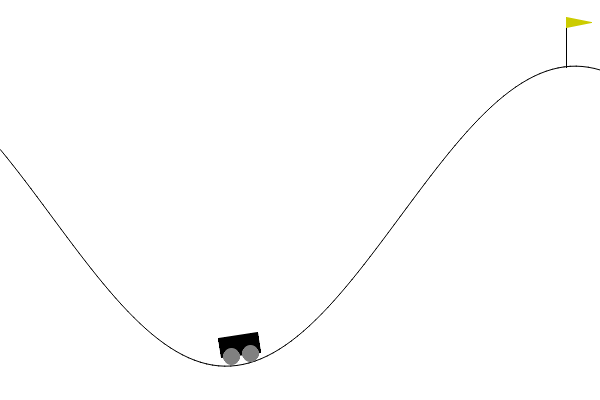
Environnement : https://gymnasium.farama.org/environments/classic_control/mountain_car
Difficulté : Les mesures sont continues (position et vitesse). Surtout, la fonction coût / récompense, est nulle pour la plupart des paires état-action (sparse reward).
Etape 1 : Discrétiser les mesures pour appliquer l’algorithme de Q learning tabulaire vu en cours.
6. Cart Pole (Reinforcement Learning)

Environnement : https://gymnasium.farama.org/environments/classic_control/cart_pole/
Difficulté : Les mesures sont continues (position et vitesse chariot, position et vitesse angulaire de la tige). Surtout les mesures sont nombreuses et définies sur un ensemble non borné.
Etape 1 : Appliquer l’algorithme de Deep-Q learning vu en cours.
7. Pendulum (Reinforcement Learning)

Environnement : https://gymnasium.farama.org/environments/classic_control/pendulum/
Difficulté : Les actions et les mesures sont continues (position et vitesse).
Etape 1 : Proposer et implémenter un contrôleur de l’automatique classique (étudié dans une autre U.E.).
8. Acrobot (Reinforcement Learning)
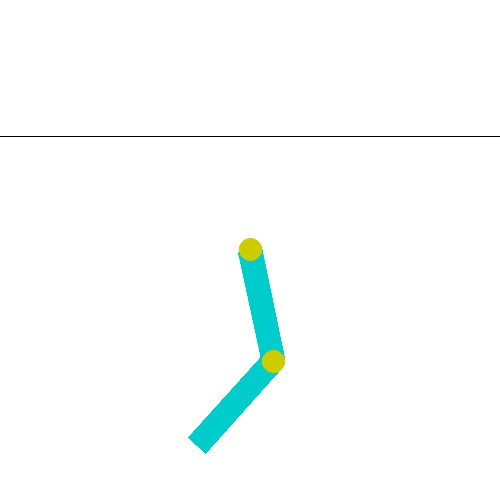
Environnement : https://gymnasium.farama.org/environments/classic_control/acrobot/
Difficulté : Les mesures sont continues et nombreuses. La fonction coût / récompense, est nulle pour la plupart des paires état-action (sparse reward).
Etape 1 : Appliquer l’algorithme de Deep-Q learning vu en cours.